You may know how to write content for a website. But to create high-quality content that ranks high on Google’s SERPs is a different ballgame. It requires an SEO content strategy with target keywords (that aren’t just the highest volume and lowest keyword difficulty), optimization, and unique storytelling for each piece to connect with your audience.
SEO content writing is a major facet of digital marketing today. If you aren’t writing for search engine optimization and your consumers effectively, your brand is essentially invisible online in a competitive digital market.
Here’s how to write content for your website to improve its performance in the SERPs and better support your bottom line.
How to Write Website Content That Ranks
Brands often make mistakes when writing website content, like spammy sales language in informational blogs or keyword stuffing on service pages that doesn’t sound natural. It can do the opposite of what you’re trying to achieve with your SEO since Google doesn’t reward content that isn’t relevant or helpful.
While you’re writing content for Google, you must have your audience’s questions, concerns, and pain points in mind to have high-ranking content. Remember, you’re still writing for humans—not just search engines!
Below is a step-by-step guide on how to write content for a website to achieve higher rankings.
Create a Content Outline to Structure the Web Page
Before you begin writing SEO website content, create an outline first. It acts as a template for everything you need from start to finish to ensure you don’t make mistakes or miss any crucial steps along the way.
Create Your Web Page’s Content Structure
Whether it’s web copy or a blog post, most SEO content structures are similar in their processes.
When creating your outline, include the following placeholders to fill in as you go:
- Title
- Target and secondary keywords with volume and keyword difficulty
- Internal links
- External links
- Headings
- Call to action (CTA)
- Estimated word count
Content outlines will differ in detail depending on the type you’re creating. For example, product page copy is short-form and will most likely use social proof as their external links. On the other hand, blogs will link to external reputable resources and can be short or long-form.
Keep in mind that you’ll update this as you go, and an outline shouldn’t be set in stone as you may discover new information when writing.
Understand Your Content Goals and Target Audience

Do you know the goals for the content you’re creating and who you’re trying to reach? If you don’t know the strategic importance of each piece of content you’re creating, it won’t be effective and can negatively impact its SEO performance.
When you have a topic that you want to write about, ask yourself, “Who are the readers of this content?” If you don’t know the exact audience demographics, reference the content marketing funnel.
By creating unique content for each funnel stage, you can meet your users where they are in their buyer’s journey. Some consumers may be ready to buy in the bottom funnel and want a straightforward answer before purchasing instead of reading an in-depth top-funnel blog.
Others may be in the middle funnel stage and want an accurate comparison between two products that aren’t clearly biased to make a better purchase decision.
Here’s where common SEO content categories fall in the marketing funnel:
- Top-Funnel (Awareness): How-to’s, informational videos, etc.
- Middle-Funnel (Consideration): Comparison blogs, complete guides, case studies, etc.
- Bottom-Funnel (Decision): Paid search ads, product pages, landing pages, etc.
When you understand your content goals and reader demographics for each piece, you can better solve their needs. It also sets you up for better success during keyword research, so you select the right search intent based on the funnel stage you’re writing in—which we’ll dive into more below.
Choose Your Web Page’s Topic
After determining your content goals, target audience, and funnel stage, brainstorm a general topic of what you want it to cover. This is the first step you’ll take when starting keyword research. You’ll end up finalizing the topic later once you have a target keyword.
Conduct Keyword Research for Target and Secondary Keywords
As mentioned above, your keyword research should do more than select the ones with the lowest keyword difficulty and highest search volume. While these attributes can find you great SEO opportunities, they shouldn’t be the only factors to consider if you want to target the best keywords in your content.
Below is a step-by-step process for effective keyword research and avoiding common mistakes.
Perform a Competitor SERP Analysis
In the first step of your keyword research, search for your general topic on Google and review the top SERPs—those are your direct competitors for this content piece. Also known as a competitor SERP analysis, it provides insights that Google is showing you what qualifies as top-ranking content for that topic. It’s like finding out the secret SEO sauce.
However, this doesn’t mean to copy what your competition is doing exactly. Google doesn’t reward duplicate content without added value, either.
Analyze the attributes that contribute to their higher rankings and see what they all share in common, including:
- Word count
- Headings
- Backlinks
- Visuals
Also, look for key details they might be missing where you can position your SEO content to outrank. Remember, Google prioritizes helpfulness and relevance. If you find that the competition is only providing surface-level details on the topic or lacks infographics to visually support the content, this can help your website rank higher in the SERPs.
Run a Competitor Content Audit
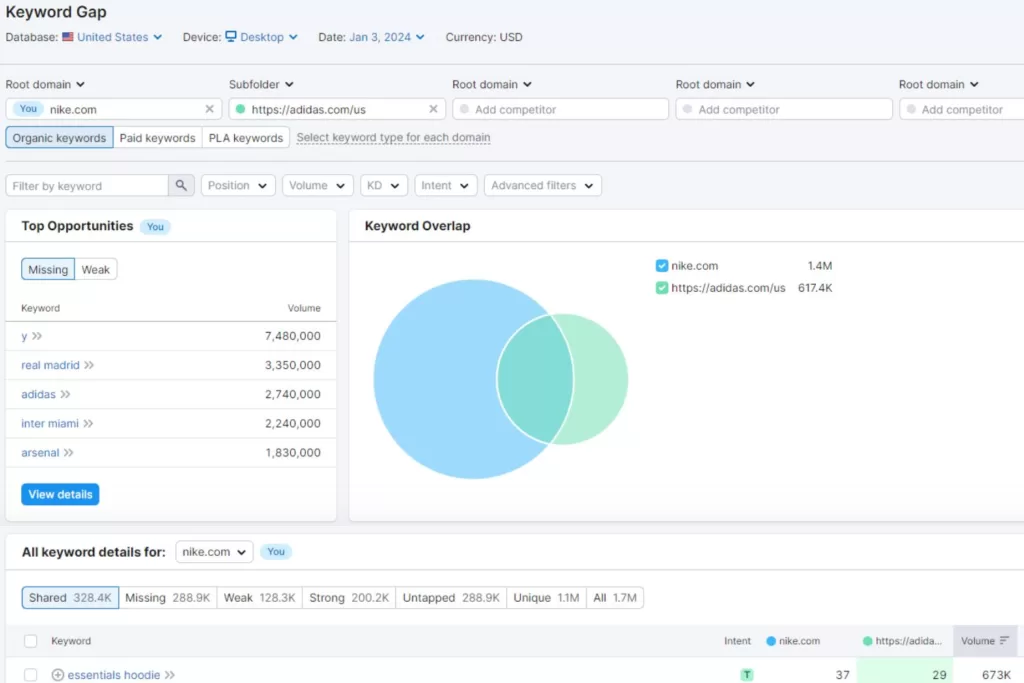
Next, take those top-ranking pages you found and do a content audit. Utilize SEO tools, like SEMRush and Ahrefs to analyze its performance. They have features like content gap and backlink analysis to see what’s contributing to its high SERP ranking with recommendations you can do to outrank.
Check for the following during a competitor content audit:
- Backlinks: Check which sites are linking to their page and their Domain Authority so you can try to earn a backlink from them, too.
- Keywords: Look at the keywords they used and build a keyword list to optimize yours with it, too.
- Performance: Analyze the content’s performance metrics, including traffic and engagement (clicks, comments, shares) to measure the topic’s success.
With this approach, you’ll be able to streamline your keyword research process next.
Conduct Keyword Research
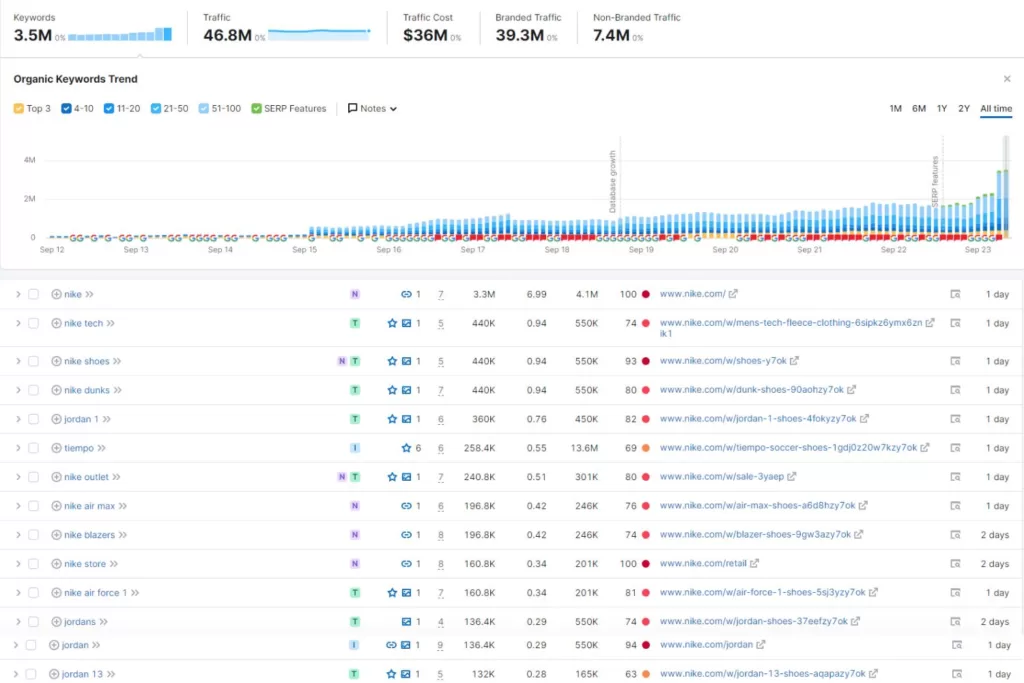
After a competitor SERP analysis and content audit, you now have a base list of target keywords. Don’t just copy the competition’s keyword lists. One of the most common mistakes brands make with keyword research is wrong search intent—the general reason behind a user’s search query.
While some content has mixed search intent, it’s not always the best-case scenario. For example, if you optimize a top-funnel (informational) blog with bottom-funnel (transactional) keywords, it can turn users away because it’s not relevant to what they’re searching for. They’re looking for helpful information, not product pages or shopping ads.
Remember, Google doesn’t reward irrelevancy if you use the wrong keyword search intent for your SEO content. Confirm the keywords are aligned with your content’s funnel stage by comparing the search intent.
Search intent keyword examples include:
- Informational (Top Funnel): how-to, what is, tips
- Commercial (Middle Funnel): brand vs. brand, best recommendations
- Navigational (Bottom Funnel): directions, branded keywords
- Transactional (Bottom Funnel): for sale, buy, discount
You can also automate this process with SEO platforms, which tell you a keyword’s search intent. This way you know which keywords to use based on the persona’s funnel stage you’re targeting.
In addition to search intent and standard keyword metrics, like search volume and keyword difficulty, look for other types of keywords that can boost your content’s performance. Long-tail and question-based keywords are also effective keyword research strategies for SEO content writing.
According to a study, 92% of search queries use long-tail keywords to find more specific results. Keywords with low search volume and keyword difficulty can also be great low-hanging fruit opportunities to boost organic traffic in your website’s content—so don’t rule those out!
From there, you can build your finalized keyword list to select your focus and secondary keywords to optimize your content.
Update Your Content Outline
Now that you have your target and secondary keywords set, go back to your outline to update your content structure:
- Create a title with your target keyword and search intent in mind
- Write headings with focus and secondary keywords naturally
- Add external and internal links you want to include
This outline will be the foundation you’ll need to finally start writing website content.
Write E-E-A-T Content With Your Audience in Mind
With the preliminary steps complete, you can now begin your SEO content writing process. If you don’t know how to write content for a website, reference Google’s E-E-A-T framework. It’s their content model that can help you create helpful and relevant information that their algorithms prioritize.
E-E-A-T stands for Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness. It’s designed to provide users with a higher standard of content and a better search experience when looking for information online.
SEO Content Writing Mistakes to Avoid
Many businesses always reference “high-quality content,” but do you know what that entails?
Examples of low-quality E-E-A-T content include:
- Copying competitor content without added value
- Long paragraphs with more than 5+ rows
- Using too many internal links
- Disorganized heading structure
- Bullet point lists with no transition text in between
All the efforts you put into writing content for your website can harm its SEO performance if you’re making these mistakes when creating it.
How to Write Content for Your Website Effectively
With an understanding of SEO writing mistakes to avoid, here are the best practices you should follow.
Examples of high-quality E-E-A-T content include:
- Easy Readability: Small paragraphs and bullet point lists to share information in a visually digestible way.
- Organized Headings: Users should be able to quickly scroll through your web page and know what it’s about.
- Supportive Visuals: Aim for helpful infographics or use stock images relevant to your topic.
- Compelling Storytelling: Grab users’ attention with a hook statement in the introduction, a persuasive CTA in the conclusion, and smooth flows in between.
You want to keep your readers engaged, so don’t make it harder for them to understand your content when it’s the solution they’re searching for.
Optimize Your SEO Website Content for Google

Once your content is complete, you must optimize it with on-page, off-page, and technical SEO. Optimization ensures search engines discover your content and provide it to users when using related search queries to your topic.
Optimize for On-Page SEO
On-page SEO is straightforward. It means optimizing the content on the physical page itself and involves a few different steps.
Keyword Optimization
Optimize your content with your target and secondary keywords naturally throughout the text. The amount of keywords you use should balance with your word count. Also known as keyword density, this prevents you from over-optimizing your content. As a rule of thumb, add one to two keywords for every 100 words.
Also, aim to have your target keyword as close to the introduction as possible naturally. It’ll help Google and your audience know what your content is about instantly.
In addition to your content, optimize your keywords in your metadata. This is the language that Google uses to better understand your content.
Best keyword optimization practices for metadata should include:
- Title Tag: Keep within 60 characters to prevent it from being cut off in preview texts. Use your focus keyword.
- Meta Description: Keep between 50 to 160 characters and use engaging language that persuades users to click through, like CTAs or a short summary of the solutions they’re seeking. Use your focus keyword.
- Image Alt Tag: Keep it around 140 characters and use descriptive language so it’s accessible for all users online to understand. Look at the image and close your eyes to better describe it. Use your focus and secondary keywords when possible.
- URL Slug: Keep between three and 250 characters, and don’t use special characters other than dashes. Use your focus keyword.
Keep all metadata sounding as natural as possible so it doesn’t sound forced by keyword stuffing.
Link Optimization
Like keyword density, your link optimization should also consider your word count. As best practice, aim to have five to six internal links per page to prevent overoptimization. Internal links help keep users on your website by navigating them to other helpful information related to the topic.
Add internal links to other blogs, case studies, and CTA in the conclusion—which is often a contact form, service page, or products. Use rich anchor text that’s relevant when hyperlinking to encourage users to click through so they know what the other page is about.
For external links, one to three per page is a rule of thumb. Always use reputable resources with high Domain Authority (60 and above) so Google recognizes your content as an authoritative and trustworthy resource—aka, E-E-AT. You can also use external links that your competitors are using from your content audit when possible.
Now you can finally publish your SEO content!
Optimize for Off-Page SEO
Off-page SEO is the optimization that occurs off your website. Examples of off-page SEO include social media posts and link building. However, the first step after publishing your content is ensuring that Google and users can discover it.
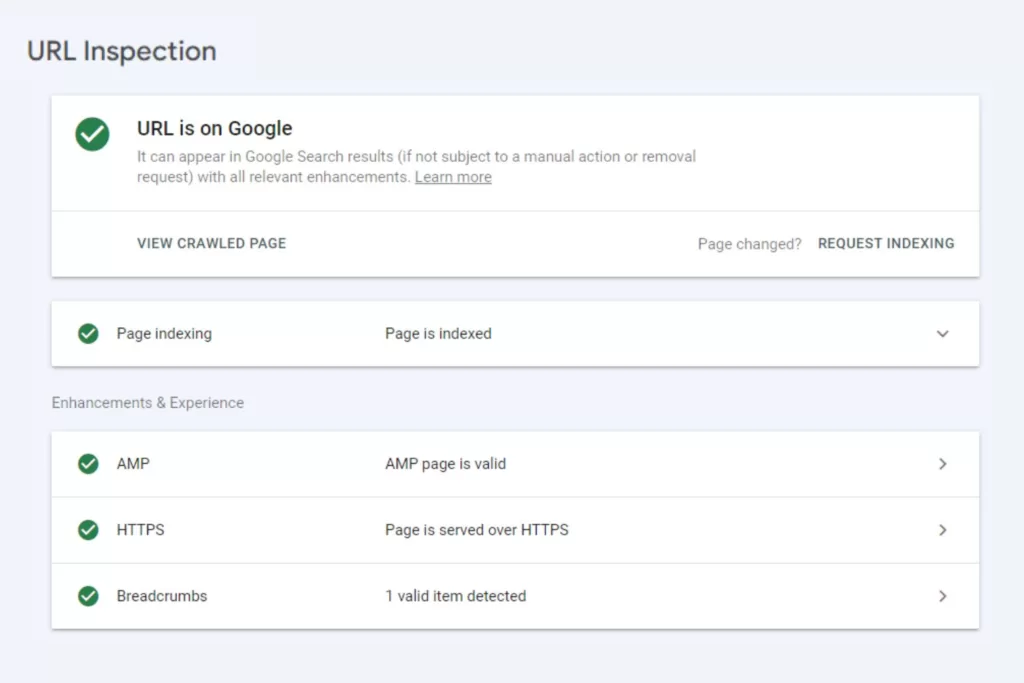
Request Indexing for Google
Once your content is published, always request indexing on Google Search Console (GSC). If Google can’t crawl (find your content) and index it (store it in their database), neither will your audience. You can monitor the status in GSC to see if there are any issues that Google has with crawling or indexing it.
Common indexing issues include broken links like 404 errors and duplicate content. GSC will provide reports so you know how to fix them, like replacing or removing broken links and editing duplicate content.
Invest in Effective Link Building
Link building is arguably one of the most important ranking factors on Google. When websites with high Domain Authority link to your site, it shows Google that you are an authoritative and trustworthy resource within your niche. In return, it generates referral traffic that has more qualified leads since a brand they trust is referring your company.
Go above cold email outreach and utilize more effective link building strategies:
- Social Media Posts: Offer cross-promotional social media shoutouts or include them in a campaign post.
- Podcast Interviews: Find industry experts within your specific niche to form better relevancy for your target audience.
- Broken Link Building: Contact websites you want to earn a backlink from by notifying them of broken links and offering to swap them with your site’s content.
When you only cold email outreach, you’re essentially asking for a favor as a stranger. Provide something of value in exchange instead.
Optimize for Technical SEO
Technical SEO is what happens behind the scenes of your website. This type of optimization helps how your web pages are displayed and ensures they provide a strong user experience (UX). In addition to easy content readability, it should be simple to navigate too.
Include the following in your technical SEO optimization:
- Website Speed: Compress large image files or remove lengthy videos that aren’t adding value. Test the speed afterward on Google PageSpeed Insights for mobile and desktop.
- Mobile Design: Test how your published content looks and performs on mobile to ensure it’s easy to read and navigate on all devices with breadcrumbs.
- Website Analytics: Check if your site’s performance has a high bounce rate or low engagement. You can also review your top-performing pages and use those as a reference.
Users nowadays will quickly leave for a competitor’s site if your site has poor UX, making technical SEO a crucial part of your content strategy.
Reach Your Website Ranking Goals with Professional SEO Content Writing
While anyone can technically write website content, that doesn’t always mean it’ll give you the results you’re looking for. At Reach Marketing Pro, our SEO services include professional SEO content writing and optimization. We also focus on your website’s functionality so your content provides a stronger user experience.
Whether you need a persuasive product page or a compelling case study to showcase your successful track record, we can help you create high-quality SEO content your website needs to stand out.
Our team will keep you informed throughout the content creation and optimization process with monthly performance reports to measure and track success.
Ready to reach your SEO content writing goals?
Contact us to get better website content that ranks today!

